|
1. Standing up straight
This fellow is leaning too far to one side.
Muscles on one side of his body are tighter than
the corresponding muscles on the other side.
In short, his skeleton is out of
alignment. |
 |
|
|
|
|
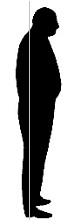
2. Standing side on
This fellow's head is too far forward -
symptomatic of hamstring and buttock muscles
that are too tight. That would explain why he
had a sore neck and a crook back. |
 |
|
TIGHT MUSCLES ATTACHED TO YOUR PELVIS
3.
Tight calf and hamstring muscles
|
|
When you sit up against a wall
with legs straight,
see how close you can get your bottom to the
wall.
You'll get a distinct impression as to which
muscles are tight when you push your bottom
closer to the wall.
Think calf and hamstring
muscles. |
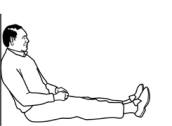
Poor
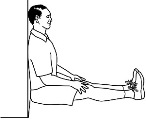
Good |
|
|
|
|
4.
Tight buttock muscles
Can sit up straight with your legs crossed and
your hands clasped
behind your back?
Is one buttock muscle is tighter than the other? |

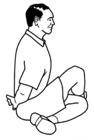
Poor Good |
|
|
|
|
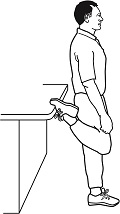
5.
Tight quadriceps muscles
Place one foot on the kitchen
bench and lean back. Most people find that they
have an excruciating quadriceps muscles and have
difficulty keeping both knees together while
doing the exercise.
If you can't keep your knees
together your abductors -0 the muscles on the
side of your thigh are too tight.
If quadriceps muscles are tight,
chances are you're also experiencing knee pain. |
 |
|
6.
Tight muscles at the front of your pelvis - the
adductors (the muscles than bring your legs
together).
|
|
This is a tough assignment for
people with tight hip flexor muscles.
The starting position is resting
on your hands with your knees as wide apart as
you can get them and feet together.
Keeping your toes on the floor,
lower your abdomen and chest to the floor and
rest your head on your hands.
The distance between your abdomen
and the floor is an indicator of how tight your
hip flexors are. to the floor |
 |
|
7. Tight hip flexors - the
muscles that lift your thigh bone.
|
|
When easing your way forward in
this position you'll feel just how tight the hip
flexor (groin) muscle is.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
8.
Tight abdominal muscles
You'll know if you have tight
abdominal muscles by determining how far off the
ground you can lift your chest. |
 |
|
GENERAL MOBILITY EXERCISES
AND MUSCLE TESTS
It is highly likely that in some of the
stretch positions some muscles will be extremely tender.
Here are the areas that are likely to be painful when
given a firm finger massage by someone else.
It is likely that one side will be
tighter than the other.
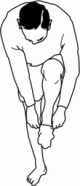
9. Tight muscles throughout
the back side of your body
|
|
Can you put your socks on while standing on one
leg?
If you can't, you've definitely tightened up -
hamstring, buttock and back muscles. |
 |
|
|
|
|
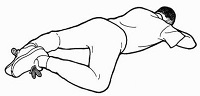
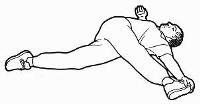
10. Super hip and thigh stretch
Can you hold on to the toe of a straight right
leg with the hand of your left arm - with right
shoulder on the floor?
Most people can't do this because the muscles of
their calves, hamstrings, buttocks and back are
too tight.
|
|
|
|
|
|
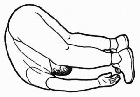
11. Heels over head
Most people had no trouble doing
this exercise when they were 10 years old.
Decades without doing it will
reveal just how tight the muscles on the back
side of your body have become. |
 |
|
|
|
|
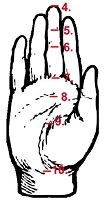
12. Hip Crossover
Put the side of the heel of the right foot up
toward the top of your left knee.
Then drop the knee and the foot down onto the
floor. Push your right knee away from your body,
opening up groin.
Repeat with the other side.
Do you find it easy to get your feet and knees
onto the floor?
Is one side tighter than the other?
Does it hurt when someone gives you a vigorous massage on your buttock (see red spot)? |

If you suffer from
lower back pain chances are you'll find it
painful when massaged in the red-spot area. One
side will probably be tighter than the other. |
|
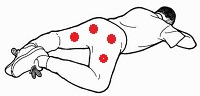
13. Tight
and painful hamstring muscles
|
|
If you suffer from lower back pain chances, when
you are in the prone frog position, chances are
you'll find it painful when massaged in the
red-spot (buttock and hamstring) areas. One side
will probably be tighter than the other. |
 |
|
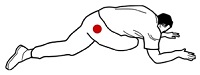
14. Tight
and painful buttock muscle
|
|
Start
on hands and knees. Put your left knee over the
right leg, so your left leg is extended and the
left knee and the laces of your shoe are on the
floor.
Then
slide the left knee and foot back as far as you
can on the floor.
You'll
feel the stretch in the right buttock muscle.
When massaged vigorously it may be painful.
|
 |
|
SHOULDERS AND HEAD
|
|
15. Shoulder, wrist and hand
test
Stand with your heels, backside
and shoulders against the wall.
See if you can get the back of your forearms and
hands comfortably against the wall when in the
'surrender' position.
If you can't there's a good chance your
hamstring and buttock muscles are too tight -
plus your shoulders need loosening up. |
 |
|
|
|
|
16. Head alignment
Stand with your heels, backside and shoulders
against the wall.
Then place your head against the wall. Are you
looking straight out in front of you or are you
looking up at the ceiling? |

 |
|
GENERAL FLEXIBILITY TEST
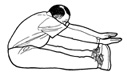
17. General test
of the flexibility of the muscles on the back
side of
your
body |
|
With legs straight and back of
knees on the floor, how far can you reach
forward toward your toes. Do this with shoes on.
The scoring goes like this:
|
0. |
Can't touch toes. |
|
|
|
|
4. |
Fingers just touch end of
toes. |
|
|
|
|
6. |
First knuckle reaches end
of toes |
|
|
|
|
7. |
Second knuckle reaches
end of toes. |
|
|
|
|
7. |
Bottom of fingers reaches
toes. |
|
|
|
|
9. |
Half way between bottom
of fingers and thumb. |
|
|
|
|
10. |
Level with thumb. |
|
|
|
|
11. |
Wrists reach end of toes |
|
 |
|
STRENGTH
TESTS
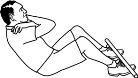
1. Situps, feet
held - general test of front of body strength |
|
How many situps can you do?
Start with feet flat (and held down) knees up,
arms crossed and hands clasping shoulders.
Sit up so your elbows touch the your knees. |
 |
|
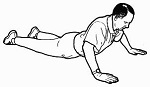
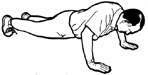
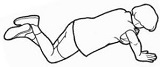
2. Pressups - general test of
trunk, upper body and arm strength |
|
How many pressups can you do - men on toes and
women on thighs?
How many pressups you can do correlates highly
and positively with lower back function. |
 |
|
3. Squats - general test of
leg strength particularly quadriceps and
buttock muscles. |
|
How many times can you squat up and down, with
your backside at least midway between you knees
and your ankles. |
 |
|
|
























